|
|
|
Experimental
Active Noise Control
in a One-Meter Box |
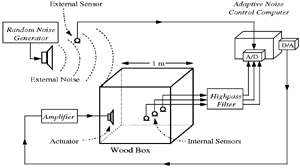
 |
Broadband noise is generated by an
external speaker and sensed by an external microphone.
|
 |
An internal speaker (actuator) is
driven by the ANC computer.
|
 |
Sample-and-hold rate: 2500Hz
|
 |
Adaptive Lattice Filter of order 14
selects control gains to minimize noise at internal microphones.
|
 |
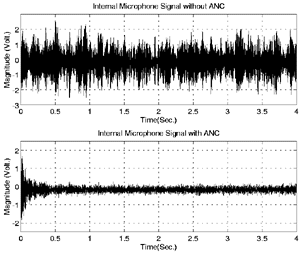
Lattice Filter converges to
near-optimal gains in 0.1 sec, optimal gains in 0.25 sec. |
|
S.-J. Chen and J. S. Gibson, “Feedforward adaptive noise control with
multivariable gradient lattice filters,” IEEE Transactions on Signal
Processing, vol. 49, pp. 511–520, March 2001.
C.-F. Wu and J. S. Gibson, “Blind identification and deconvolution for IIR
channels,” IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, December 1998.
S.-J. Chen, J. Lew, J.S. Gibson, and C.-M.
Ho, “Cancellation of noise in an acoustic experiment by an adaptive lattice
filter.”
![]()